

 Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of compute
power, database storage, applications, and other IT resources through a cloud services
platform via the internet. Companies offering these computing services are called
cloud providers and typically charge for cloud computing services based on usage,
similar to how you are billed for water or electricity at home (pay-as-you-go pricing).
A cloud services platform provides rapid access to flexible and low cost IT resources.
With cloud computing, you don’t need to make large upfront investments in hardware
and spend a lot of time on the heavy lifting of managing that hardware. Cloud computing
services all work a little differently, depending on the provider. But many provide
a friendly, browser-based dashboard that makes it easier for IT professionals and
developers to order resources and manage their accounts. Some cloud computing services
are also designed to work with REST APIs and a command-line interface (CLI), giving
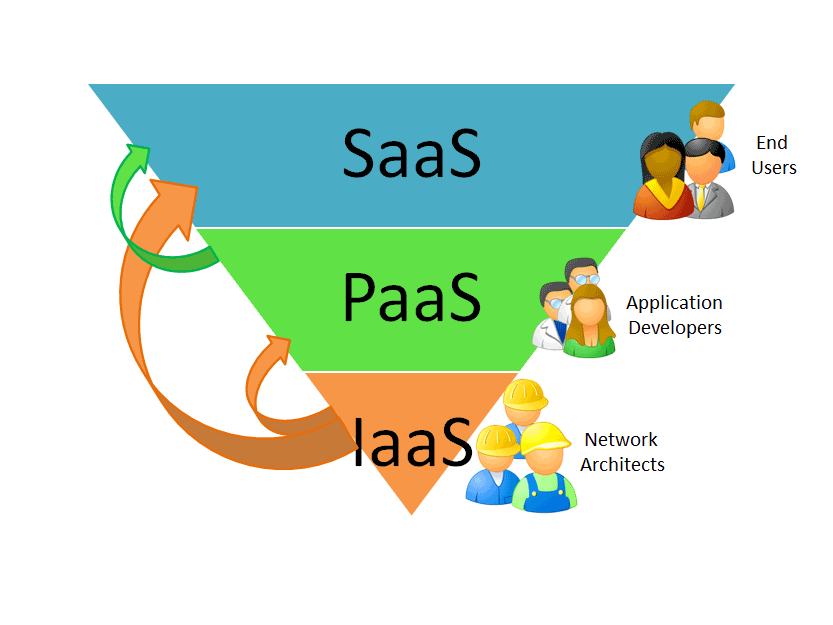
developers multiple options. Cloud computing has three main types that are commonly
referred to as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS),
and Software as a Service (SaaS).
Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of compute
power, database storage, applications, and other IT resources through a cloud services
platform via the internet. Companies offering these computing services are called
cloud providers and typically charge for cloud computing services based on usage,
similar to how you are billed for water or electricity at home (pay-as-you-go pricing).
A cloud services platform provides rapid access to flexible and low cost IT resources.
With cloud computing, you don’t need to make large upfront investments in hardware
and spend a lot of time on the heavy lifting of managing that hardware. Cloud computing
services all work a little differently, depending on the provider. But many provide
a friendly, browser-based dashboard that makes it easier for IT professionals and
developers to order resources and manage their accounts. Some cloud computing services
are also designed to work with REST APIs and a command-line interface (CLI), giving
developers multiple options. Cloud computing has three main types that are commonly
referred to as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS),
and Software as a Service (SaaS).
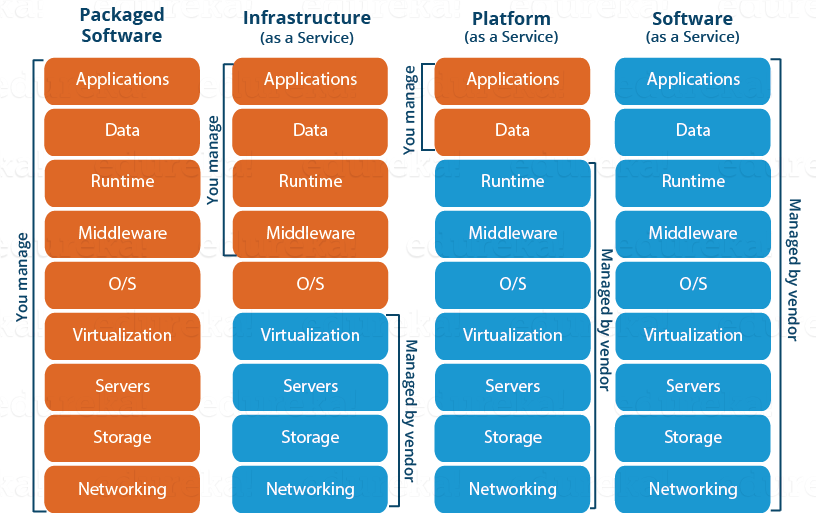
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
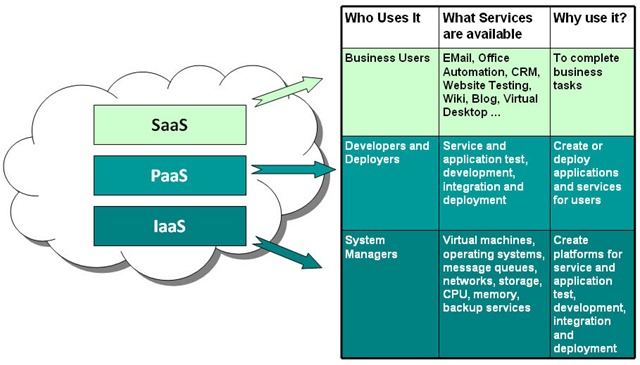
 IaaS contains the features that provide access to networking
features, computers (virtual or on dedicated hardware), and data storage space.
Infrastructure as a Service provides you with the highest level of flexibility and
management control over your IT resources
IaaS contains the features that provide access to networking
features, computers (virtual or on dedicated hardware), and data storage space.
Infrastructure as a Service provides you with the highest level of flexibility and
management control over your IT resources
Platform as a Service (IaaS)
 PaaS remove the need for organizations to manage the
underlying infrastructure (usually hardware and operating systems) and allow you
to focus on the deployment and management of your applications. This helps you be
more efficient as you don’t need to worry about resource procurement, capacity planning,
software maintenance, patching, or any of the other undifferentiated heavy lifting
involved in running your application.
PaaS remove the need for organizations to manage the
underlying infrastructure (usually hardware and operating systems) and allow you
to focus on the deployment and management of your applications. This helps you be
more efficient as you don’t need to worry about resource procurement, capacity planning,
software maintenance, patching, or any of the other undifferentiated heavy lifting
involved in running your application.
Software as a Service (IaaS)
 SaaS provides you with a completed product that is run
and managed by the service provider. In most cases, people referring to Software
as a Service are referring to end-user applications. With a SaaS offering you do
not have to think about how the service is maintained or how the underlying infrastructure
is managed; you only need to think about how you will use it. Example, Web-based
email is a SaaS application where you can send and receive email without having
to manage feature additions to the email product or maintaining the servers and
OS that the email program is running on.
SaaS provides you with a completed product that is run
and managed by the service provider. In most cases, people referring to Software
as a Service are referring to end-user applications. With a SaaS offering you do
not have to think about how the service is maintained or how the underlying infrastructure
is managed; you only need to think about how you will use it. Example, Web-based
email is a SaaS application where you can send and receive email without having
to manage feature additions to the email product or maintaining the servers and
OS that the email program is running on.
 Advantages
Advantages
1. Trade capital expense for variable expense:
Only need to pay when you consume computing resources, and only pay for how much
you consume. 2. Benefit from
massive economies of scale: Usage from hundreds of thousands of customers are
aggregated in the cloud, providers can achieve higher economies of scale which translates
into lower pay as you go prices. 3. Stop guessing capacity: When you make a capacity decision
prior to deploying an application, you often either end up sitting on expensive
idle resources or dealing with limited capacity. With cloud computing, these problems
go away. You can access as much or as little as you need, and scale up and down
as required with only a few minutes’ notice. 4. Increase speed and agility: you can reduce the time
it takes to make those resources available to your developers from weeks to just
minutes. This results in a dramatic increase in agility for the organization, since
the cost and time it takes to experiment and develop is significantly lower.
6. Reliability:
Cloud computing makes data backup, disaster recovery and business continuity easier
and less expensive, because data can be mirrored at multiple redundant sites on
the cloud provider’s network. 7. Global scale in minutes: Delivering the right amount
of IT resources (such as more or less computing power, storage, and bandwidth) right
when it’s needed and from the right geographic location.
Cloud deployment model
A cloud deployment model represents a specific type of cloud environment, primarily
distinguished by ownership, size, and access. Mainly there are four different ways
to deploy cloud computing resources: public cloud, private cloud, hybrid cloud and
community cloud.
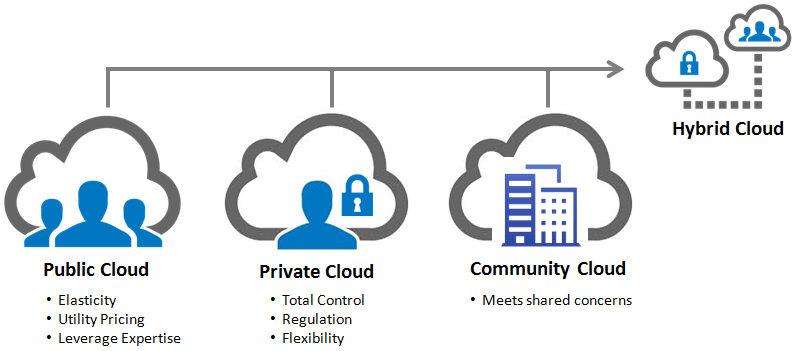 Public Cloud : Public clouds are owned and operated by a third-party cloud
service provider, which deliver their computing resources like servers and storage
over the Internet. With a public cloud, all hardware, software and other supporting
infrastructure is owned and managed by the cloud provider. You access these services
and manage your account using a web browser.
Public Cloud : Public clouds are owned and operated by a third-party cloud
service provider, which deliver their computing resources like servers and storage
over the Internet. With a public cloud, all hardware, software and other supporting
infrastructure is owned and managed by the cloud provider. You access these services
and manage your account using a web browser.
Private Cloud : A private cloud refers to cloud computing resources used
exclusively by a single business or organization. A private cloud can be physically
located on the company’s on-site datacenter. Some companies also pay third-party
service providers to host their private cloud.
Hybrid Cloud : Hybrid clouds combine public and private clouds, bound together
by technology that allows data and applications to be shared between them. By allowing
data and applications to move between private and public clouds, hybrid cloud gives
businesses greater flexibility and more deployment options. i.e, a cloud consumer
can be choose to deploy cloud services processing sensitive data to a private cloud
and other, less sensitive cloud services to a public cloud.
Community Cloud : The model type community cloud shares the cloud infrastructure
across several organizations to support specific community having common concerns.
In this model, cloud infrastructure is provided on the premises or at the data center
owned by third party. This is managed by participating organizations or third party.
Uses of cloud computing
 You are probably using cloud computing right now, even if you don’t realize it.
If you use an online service to send email, edit documents, watch movies or TV,
listen to music, play games or store pictures and other files, it is likely that
cloud computing is making it all possible behind the scenes. You can use cloud computing
for following,
You are probably using cloud computing right now, even if you don’t realize it.
If you use an online service to send email, edit documents, watch movies or TV,
listen to music, play games or store pictures and other files, it is likely that
cloud computing is making it all possible behind the scenes. You can use cloud computing
for following,
8 Create new apps and services
8 Store, back up and recover data
8 Host websites and blogs
8 Stream audio and video
8 Deliver software on demand
8 Analyze data for patterns and make predictions
Copyright © Qpsoftec Technologies. All rights reserved | Privacy Policy